- myc - Burkitts + B & T-cell lymphomas
- bcl2 = follicular B-cell lymphoma
- bcl3 = chronic B-cell lymphoma
- bcl6 = diffuse B-cell lymphoma
- any other genes = acute T-cell lymphoma
Sunday, May 27, 2012
B-cell lymphoma genetic links
Genetics of lymphomas - translocations cause overexpression of the following genes which cause the disease:
Friday, May 25, 2012
Kartagener's Syndrome
Here's another eponymous syndrome named Kartagener's (German physician, 1933)*. It's a triad of features:
Here's my random picture for remembering this syndrome:
* Kartagener M (1933). "Zur Pathogenese der Bronchiektasien: Bronchiektasien bei Situs viscerum inversus". Beiträge zur Klinik der Tuberkulose. 83 (4): 489–501.
* also... Situs Solitus is the normal positioning of organs in the body.
- Dextrocardia or Situs inversus
- Brochiectasis
- Recurrant sinusitis
Here's my random picture for remembering this syndrome:
This heart (dextrocardia) in a cart (Kartageners) was traveling past a wrong way sign (..a..situs...sinusitis) and crashed into a tree (broken tree = broken bronchial tree = bronchiectasis).
* Kartagener M (1933). "Zur Pathogenese der Bronchiektasien: Bronchiektasien bei Situs viscerum inversus". Beiträge zur Klinik der Tuberkulose. 83 (4): 489–501.
* also... Situs Solitus is the normal positioning of organs in the body.
Thursday, May 24, 2012
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis
Disease of the immunocompromised. Acute onset focal neurological deficit, usually hemispherical (hemiparesis, visual field disturbance). Can be accompanied by fever. Imaging shows characteristic ring-enhancing lesions:
Labels:
Neuro
Monday, May 21, 2012
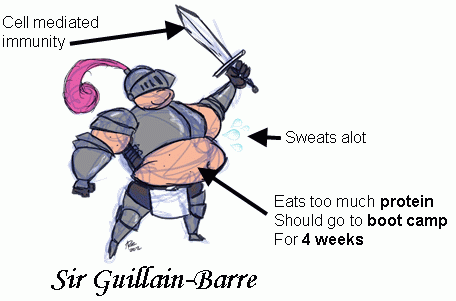
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Another eponymous syndrome named by a French physician at the turn of the century.
* boot camp - to reflect that neuropathy often begins in feet (boot) and most commonly caused by CAMPylobacter Jejuni.
** also note pronounciation - gwee-awn barr-ay (in your best french accent)
- It is an acute, inflammatory, post-infectious, ascending polyneuropathy (2:100,000).
- Caused by (??): post viral (often: Campylobacter jejuni or CMV) cell mediated response against peripheral gangliosides.
- Polyneuropathy begins peripherally and progresses centrally - if it reaches respiratory/bulbar areas this is bad.
- Often causes autonomic dysfunction (sweating, tachycardia, dysrhthmias)
- CSF shows lots of protein (>5.5g/L)
- Develops over around 4 weeks.
- Most important investigation: spirometry
* boot camp - to reflect that neuropathy often begins in feet (boot) and most commonly caused by CAMPylobacter Jejuni.
** also note pronounciation - gwee-awn barr-ay (in your best french accent)
Sunday, May 20, 2012
Pleural Effusions
Pleural effusions can be exudative (>30g/L protein) or transudative (<30g/L protein). Things that commonly cause effusions of each type are:
Also light's criteria - if any of the following are true then = exudative:
Also light's criteria - if any of the following are true then = exudative:
- Pleural/Serum protein ratio > 0.5
- Pleural/Serum LDH ratio > 0.5
- Pleural fluid LDH > 2/3 of serum LDH level.
Labels:
Resp
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)